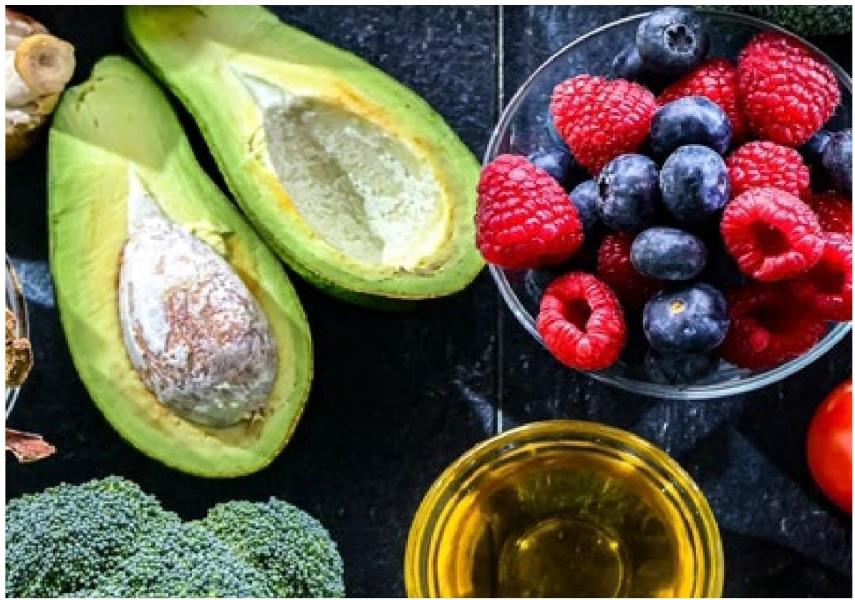
AS OF 2023, AN ESTIMATED 24.3% OF ADULTS IN THE UNITED STATES LIVE WITH CHRONIC PAIN AND 8.5% report significant limitations in work and activities of daily life, highlighting chronic pain as a serious public health concern and economic issue. Chronic pain conditions contribute to rising healthcare costs, decreased productivity in the workplace, and increased mental health concerns.
An aging population, sedentary lifestyles, and inflammatory diets are key factors in the rising prevalence of chronic pain. Despite varied etiologies, nutritional support offers a non-pharmacological, patient-centered approach that complements chiropractic care and can effectively support pain relief and functional recovery.
Proper nutrition targets inflammation, supports tissue healing, and enhances physiological resilience. The following strategies outline specific nutritional interventions that can help prevent and treat chronic pain.
• Anti-inflammatory Diet: Emphasize foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids like fatty fish, flaxseeds and walnuts, as well as antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables like berries and green leafy vegetables. Incorporating herbs like turmeric, garlic and ginger into meals provides phytochemicals that are rich in potent bioactive compounds. Additionally, minimize the intake of ultra-processed foods, excessive omega-6 fatty acids, and refined sugars.
• Supplemental Omega-3 Fatty Acids: EPA and DHA can downregulate inflammatory cytokines, supporting pain relief, but dietary intake of these essential fats is often low in American diets. Testing red blood cell levels of EPA and DHA through a simple omega-3 index finger-prick test can offer insight into a patient's omega-3 status and provide recommendations on appropriate supplementation.
• Turmeric: Contains curcuminoids that downregulate inflammatory cytokines. Curcuminoids may have poor absorption, so utilizing curcumagalactomannoside (CGM) technology can significantly improve its bioavailability by encapsulating the curcuminoids in fenugreek fiber. This allows the curcuminoids to bypass liver metabolism, increasing their activity in systemic circulation. Curcumin has been shown to modulate inflammation and support joint health without side effects that may occur with pharmaceutical interventions.
“Curcumin has been shown to modulate inflammation and support joint health without side effects that may occur with pharmaceutical interventions.”

• Protein: Ensuring adequate protein supports muscle recovery, ligament and tendon repair, and connective tissue health. While the current RD A for protein intake is ,8g/kg of body weight, research has shown the benefits of 1.2 g/kg for weight management, and up to 2.2 g/kg for athletes participating in resistance training.
• Manganese: A critical cofactor for collagen synthesis and tissue repair and essential during recovery from ligament sprains and muscle strains. Supplementation may be warranted in cases of increased demand, such as following a musculoskeletal injury.
• Vitamin C: Vital for collagen synthesis and maintaining structural integrity of connective tissues. Modulates cytokine activity and attenuates low-grade inflammation that is often present in chronic musculoskeletal conditions.
“Proper nutrition targets inflammation, supports tissue healing, and enhances physiological resilience.”
• Zinc: Essential mineral involved in wound healing, tissue remodeling, and collagen production.
Nutritional interventions that support nerve function and reduce neuropathic pain include:
• B Vitamins: Critical for nerve health, myelin repair, and reducing neuropathy symptoms.
• Magnesium: Involved in neurotransmission, muscle relaxation, and reduction of pain sensitization.
• Vitamin D: Deficiency has been linked to chronic musculoskeletal pain and heightened pain perception.
The gut-brain axis is increasingly recognized in the modulation of pain perception and inflammation:
• Prebiotics and Probiotics: Modulating the gut microbiome can reduce systemic inflammation, influence neurotransmitter production (serotonin, GABA), and improve gut barrier function.
• Fiber-rich Diet: Supports microbiome diversity, essential for reducing chronic inflammation and indirectly alleviating pain symptoms.
• Stool testing: Can provide valuable information regarding levels of inflammation in the gut microbiome and can influence treatment strategies to modify the environment and attenuate inflammation.
Nutrition enhances chiropractic outcomes by targeting key pain drivers such as chronic inflammation, tissue degeneration, neurological dysfunction, and gut dysbiosis. Evidence-based interventions including anti-inflammatory diets, supplementation, and gut-supportive strategies offer a non-pharmacological, patient-centered approach to reducing chronic pain and improving quality of life.

Dr. Sarah Clarke is a certified functional medicine practitioner and chiropractor. She currently serves as the Chiropractic Liaison for Standard Process, supporting clinical education and collaboration within the chiropractic and integrative healthcare communities. She earned her doctorate from Palmer College of Chiropractic West in 2015, after completing a B.A. in Psychology from Kenyon College in 2012. Drawing on her strong foundation in both mental and physical health, Dr. Clarke is especially passionate about the integration of nutrition and lifestyle factors and their impact on mind-body wellness. Dr. Clarke can be reached at (262) 495-6597, via email [email protected] or learn more at StandardProcess.com.
 View Full Issue
View Full Issue